Delivery of Services to Childhood Cancer Survivors in India: A National Survey
CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 · Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 2020; 41(05): 707-717
DOI: DOI: 10.4103/ijmpo.ijmpo_6_20
Abstract
Background: Continuum of care is an important concern for childhood cancer survivors. Studies from high-income countries indicate a significant development in services to these survivors. Similar information is unavailable from India. Methods: An online survey form was developed and sent to 86 centers. Data were collected over a 6-month period in 2017. Results: Fifty nine centers responded (44.1% private sector, 33.9% public, and 22.0% charitable trust). The services are mainly provided (91%) within routine oncology clinics. There is no upper age limit (61%) or time period limit (63%) for follow-up at most of the centers. The major barriers for follow-up are distance, lack of knowledge, lack of adequate facilities, and patient priority for follow-up. Conclusion: This survey provides baseline information on current service provided to childhood cancer survivors in India. There is a need to inform, educate, and sensitize the survivor and their family as well as improving services.
Keywords
Childhood cancer - health-care services - India - survivorshipSupplementary Material
- Supplementary Material
Publication History
Received: 09 January 2020
Accepted: 11 May 2020
Article published online:
17 May 2021© 2020. Indian Society of Medical and Paediatric Oncology. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.)
Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
A-12, 2nd Floor, Sector 2, Noida-201301 UP, India
Abstract
Background: Continuum of care is an important concern for childhood cancer survivors. Studies from high-income countries indicate a significant development in services to these survivors. Similar information is unavailable from India. Methods: An online survey form was developed and sent to 86 centers. Data were collected over a 6-month period in 2017. Results: Fifty nine centers responded (44.1% private sector, 33.9% public, and 22.0% charitable trust). The services are mainly provided (91%) within routine oncology clinics. There is no upper age limit (61%) or time period limit (63%) for follow-up at most of the centers. The major barriers for follow-up are distance, lack of knowledge, lack of adequate facilities, and patient priority for follow-up. Conclusion: This survey provides baseline information on current service provided to childhood cancer survivors in India. There is a need to inform, educate, and sensitize the survivor and their family as well as improving services.
Keywords
Childhood cancer - health-care services - India - survivorshipIntroduction
Cancer survivorship has significantly increased, particularly for childhood cancers, where 5-year survival rates in high-income countries exceeds 80%,[1] although the outcomes are more modest in India.[2] According to the National Cancer Institute, “An individual is considered a cancer survivor from the time of diagnosis, through the balance of his or her life. Family members, friends, and caregivers are also impacted, and are therefore, included in this definition.”[3] Treatment-related late effects may exhibit several complications such as learning disabilities,[4] compromised quality of life,[5] and in some cases morbidity as well as early mortality.[6]
This cohort of population should, therefore, be regarded as highly vulnerable and specialized follow-up and care should be administered. Studies from various high-income countries have indicated significant development in delivering services to these survivors. Tonorezos et al. provided models of care across 18 countries indicating the common challenges and mechanisms that have evolved in the management of childhood cancer survivors globally.[7] Among the high-income countries such as United States, Denmark, and Germany, several comprehensive survivor programs have been developed to provide follow-up and care for childhood cancer survivors.[8],[9],[10],[11],[12] The Institute of Medicine recommends evaluating and monitoring processes of service provision in cancer survivorship for pediatric oncology.[13] The follow-up services, therefore, must include dedicated survivor clinics which can enable optimal care to the survivors like: Regular screening for the late effects, psychological support, sensitizing on education and research, harmonizing the transition to adult care, planning for surveillance, guiding for education, and occupation. Besides this, these should also act as platforms for communication to release anxiety among survivors as well as family members.
Hitherto, care of childhood cancer patients in low and middle-income countries has not focused on care of survivors as well.[7] There is a lacuna in this area, including providing health insurance for cancer survivors.[14] Studies have evidenced that Indian long-term adult cancer survivors face financial constraints, social anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and depression.[15] The after completion of therapy (ACT) clinic of Tata Memorial hospital has followed 1845 childhood cancer survivors to monitor late effects, growth problems, and psychosocial problems since its inception in 1991.[16] However, there is dearth of information on practices and service delivery for child cancer survivors on a national basis in the Indian context. Our study aimed to determine the existing characteristics of service provision to childhood cancer survivors in India in terms of practice, follow-up information, and education. The present study also aimed to compare the services across public, private, and charitable trust sectors in India.
Methods
A 25-item online survey using Google Forms was developed [Appendix 1] [SUPPORTING:1]. The survey had questions pertaining to survivorship services, follow-up information, education and involvement in research for the survivors at the providing organization. Feedback on the same was requested from the Indian Pediatric Oncology Group (InPOG) Late Effects subcommittee. Subsequently, it was sent to primary/senior consultants treating children with cancer in 86 centers (one consultant per centre) in India. Introductory mails and letters were attached to the questionnaires for clarity and understanding of the survey. The feedback was collected for a 6-month timeframe in 2017. The respondents could skip the questions at their discretion. The data analysis was done based on the proportion of affirmative responses. Frequency tabulations, data visualization through charts, and graphs were presented to summarize the data. Statistical significance was determined using the Kruskal–Wallis-H test and Chi-square test for various variables. All data analysis was done using the SPSS Statistics, version 24 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA).
Results
Respondent centres
Responses from 59 (68%) centers in 24 cities were received. Of these, 26 were from private sector (response rate 74%), 20 from public sector (response rate 57%), and 13 from charitable trust (response rate 81%). The 59 centers represented, have a median range of 50–100 new pediatric oncology patients diagnosed annually [Table 1].
Delivery of services to childhood cancer survivors in India
All centers provide survivorship services. However, most of them 91.5% (n = 54) were providing care within their routine oncology clinic service, and only five centers (8.4%) have a dedicated survivor clinic. There is no upper age limit (61.01%) and no upper period time limit (63%) for follow-up of childhood cancer survivors at most of the centers, as shown in [Table 1]. Database/registry is used to capture and maintain records of the survivor population at 67.8% centers (n = 40). The following health-care professionals are usually present or accessible when providing follow-up to childhood cancer survivors in the clinic-oncologist (88%), social worker (34%), nurse (31%), endocrinologist (20%), and psychologist (20%).
The conference on guideline standardization guidelines are used by the clinicians to guide clinical practice in 54.2% centers, whereas others have no specific recommendations for providing services. Most of the centers were handing out treatment summaries to the patients (61%). The summaries contain a detail of the treatment in 80% cases, diseases and stages summary in 56% cases, follow-up care plans in 49% cases, potential health problems in 36% cases, and information leaflets in 17% of the centers [Table 1].
Compliance with follow-up and barriers
The survivor follow-up rates for 2 years and 5 years after end of the treatment shows a decline between centers, where 76.1% centers reported a follow-up by 50% and above survivors until 2 years of active treatment, whereas only 49% programs had the same percentage of patients at 5-year follow-up. The current level of service was thought to be inadequate or very inadequate 19%, neither adequate nor inadequate by 56% of centers, and adequate or very adequate 25%. The barriers to follow-up as shown in [Figure 1] according to the clinicians were mainly distance to clinic (n = 28), lack of knowledge among patients and parents (n = 22), lack of adequate facilities time/space at the center (n = 22), and patient priority for follow-up services (n = 18).
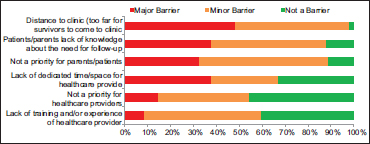
| Figure 1: Barriers to survivorship programs according to health-care providers
Comparison of services for survivors in the public, private, and charitable sector in India
There was a statistically significant difference (P = 0.05) in the patient volume among the three sectors in India [Table 1]. Dedicated survivor clinics were more common in the public sector and one in the charitable trust [Table 1]. The follow-up rates at 2 years and 5 years after the end of treatment also varied significantly (P = 0.008 and. 019, respectively) between the sectors. Follow-up rates were higher (>75% of the treated cases) in charitable trust centers (76.9%) and those in the private sector (57%) in comparison with the public sector (30%) at 2 years follow-up. Similarly, at 5 years follow-up, >75% of the treated cases came in 23% of private and 15% of charitable trust, whereas none at the public sector [Table 1]. Follow-up was happening in the public hospitals, although the proportion of survivors coming for follow-up was smaller.
Discussion
Assessing the availability and delivery of survivorship services would help understand the gaps and improve services for long-term childhood cancer survivors. The data from our study across the nation in 59 centers represents pediatric oncology services ranging from smaller to the largest programs. There is deficiency and heterogeneity in provision of services to childhood cancer survivors. Furthermore, besides the lack of resources including dedicated survivor clinics, staff, updated registries, and follow-up remain difficult to achieve.
Despite the several inadequacies in service provision, there are several initiatives that are aligned to address these gaps in India. For the first decade of the 21st century, the ACT clinic at Tata remained the only service for survivors.[15] All the other dedicated hospital survivor clinics have started in the past few years. All India Institute of Medical Sciences provides a bilingual after the treatment completion card to all patients which records the treatment given (dates, types of treatment, and cumulative doses) and possible late effects, and this is being adopted elsewhere as well.[17] Cankids as part of the passport2 life (P2 L) Project is running survivor P2 L clinics in 14 locations with the treating hospitals as well as independently. A paper and online (www.survivorp2l.org) survivor passport is being provided to all survivors. Ugam and Indian Cancer Society are doing similar work under their partnership in cancer survivorship optimization project. The InPOG-LE-16-01 study which is currently open in 13 centers and has recruited 1618 patients, is also encouraging protocol-based assessment of survivors and ensuring long-term follow-up.[18]
The limitation of the survey is that results are based on self-reporting by consultants from the participating institutes and have not been corroborated by other simultaneous efforts such as external audit of services. Furthermore, the survey questions were designed to provide a broad overview and not dissect survivorship services in detail. Such activities would be desirous in future and would have resource requirements.
Conclusion
The survey provides baseline information on current service provided to childhood cancer survivors in India. There is a need to inform, educate, and sensitize the survivor and their family as well as improving services.
Conflict of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary Material
References
- Stewart BW, Wild CW. editors World Cancer Report 2014. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2014
- Arora RS, Eden TO, Kapoor G. Epidemiology of childhood cancer in India. Indian J Cancer 2009; 46: 264-73
- About Cancer Survivorship Research: Survivorship Definitions. The National Cancer Institute. http://dccps.cancer.gov/ocs/definitions.html. Available from: [Last accessed on 2012 Oct 11]
- Mitby PA, Robison LL, Whitton JA, Zevon MA, Gibbs IC, Tersak JM. et al. Utilization of special education services and educational attainment among long-term survivors of childhood cancer: A report from the childhood cancer survivor study. Cancer 2003; 97: 1115-26
- Gurney JG, Krull KR, Kadan-Lottick N, Nicholson HS, Nathan PC, Zebrack B. et al. Social outcomes in the childhood cancer survivor study cohort. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 2390-5
- Chen MH, Colan SD, Diller L. Cardiovascular disease: Cause of morbidity and mortality in adult survivors of childhood cancers. Circ Res 2011; 108: 619-28
- Tonorezos ES, Barnea D, Cohn RJ, Cypriano MS, Fresneau BC, Haupt R. et al. Models of care for survivors of childhood cancer from across the globe: Advancing survivorship care in the next decade. J Clin Oncol 2018; 36: 2223-30
- Oeffinger KC, Eshelman DA, Tomlinson GE, Buchanan GR. Programs for adult survivors of childhood cancer. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: 2864-7
- Marr KC, Agha M, Sutradhar R, Pole JD, Hodgson D, Guttmann A. et al. Specialized survivor clinic attendance increases adherence to cardiomyopathy screening guidelines in adult survivors of childhood cancer. J Cancer Surviv 2017; 11: 614-23
- Sutradhar R, Agha M, Pole JD, Greenberg M, Guttmann A, Hodgson D. et al. Specialized survivor clinic attendance is associated with decreased rates of emergency department visits in adult survivors of childhood cancer. Cancer 2015; 121: 4389-97
- Health. Dk: Your Health Portal. http://www.sundhed.dk. Available from: [Last accessed on 2019 Dec 08]
- Escherich G, Bielack S, Maier S, Braungart R, Brümmendorf TH, Freund M. et al. Building a National Framework for Adolescent and Young Adult Hematology and Oncology and Transition from Pediatric to Adult Care: Report of the Inaugural Meeting of the “AjET” Working Group of the German Society for Pediatric Oncology and Hematology. J Adolesc Young Adult Oncol 2017; 6: 194-9
- Hewitt M, Weiner S, Simone J. Childhood Cancer Survivorship: Improving Care and Quality of Life. Washington: National Academies Press; 2003
- Balarajan Y, Selvaraj S, Subramanian SV. Health care and equity in India. Lancet 2011; 377: 505-15
- Kurkure PA, Achrekar S, Uparkar U, Dalvi N, Goswami S. Surviving childhood cancer: What next? Issues under consideration at the after completion of therapy (ACT) clinic in India. Med Pediatr Oncol 2003; 41: 588-9
- Mohanti BK, Kaur J. Living experiences of Indian adult cancer survivors – A brief report. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2015; 16: 507-12
- Seth R. The after treatment completion card (ATCC): Medical passport for pediatric cancer survivors. Pediatr Hematol Oncol J 2018; 3: 88-9
- Arora RS, Bakhshi S. Indian Pediatric Oncology Group (InPOG) – Collaborative research in India comes of age. Pediatr Hematol Oncol J 2016; 1: 13-7
Address for correspondence
Publication History
Received: 09 January 2020
Accepted: 11 May 2020
Article published online:
17 May 2021
© 2020. Indian Society of Medical and Paediatric Oncology. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.)
Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
A-12, 2nd Floor, Sector 2, Noida-201301 UP, India

| Figure 1: Barriers to survivorship programs according to health-care providers
- 1 Stewart BW, Wild CW. editors World Cancer Report 2014. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2014
- 2 Arora RS, Eden TO, Kapoor G. Epidemiology of childhood cancer in India. Indian J Cancer 2009; 46: 264-73
- 3 About Cancer Survivorship Research: Survivorship Definitions. The National Cancer Institute. http://dccps.cancer.gov/ocs/definitions.html. Available from: [Last accessed on 2012 Oct 11]
- 4 Mitby PA, Robison LL, Whitton JA, Zevon MA, Gibbs IC, Tersak JM. et al. Utilization of special education services and educational attainment among long-term survivors of childhood cancer: A report from the childhood cancer survivor study. Cancer 2003; 97: 1115-26
- 5 Gurney JG, Krull KR, Kadan-Lottick N, Nicholson HS, Nathan PC, Zebrack B. et al. Social outcomes in the childhood cancer survivor study cohort. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 2390-5
- 6 Chen MH, Colan SD, Diller L. Cardiovascular disease: Cause of morbidity and mortality in adult survivors of childhood cancers. Circ Res 2011; 108: 619-28
- 7 Tonorezos ES, Barnea D, Cohn RJ, Cypriano MS, Fresneau BC, Haupt R. et al. Models of care for survivors of childhood cancer from across the globe: Advancing survivorship care in the next decade. J Clin Oncol 2018; 36: 2223-30
- 8 Oeffinger KC, Eshelman DA, Tomlinson GE, Buchanan GR. Programs for adult survivors of childhood cancer. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: 2864-7
- 9 Marr KC, Agha M, Sutradhar R, Pole JD, Hodgson D, Guttmann A. et al. Specialized survivor clinic attendance increases adherence to cardiomyopathy screening guidelines in adult survivors of childhood cancer. J Cancer Surviv 2017; 11: 614-23
- 10 Sutradhar R, Agha M, Pole JD, Greenberg M, Guttmann A, Hodgson D. et al. Specialized survivor clinic attendance is associated with decreased rates of emergency department visits in adult survivors of childhood cancer. Cancer 2015; 121: 4389-97
- 11 Health. Dk: Your Health Portal. http://www.sundhed.dk. Available from: [Last accessed on 2019 Dec 08]
- 12 Escherich G, Bielack S, Maier S, Braungart R, Brümmendorf TH, Freund M. et al. Building a National Framework for Adolescent and Young Adult Hematology and Oncology and Transition from Pediatric to Adult Care: Report of the Inaugural Meeting of the “AjET” Working Group of the German Society for Pediatric Oncology and Hematology. J Adolesc Young Adult Oncol 2017; 6: 194-9
- 13 Hewitt M, Weiner S, Simone J. Childhood Cancer Survivorship: Improving Care and Quality of Life. Washington: National Academies Press; 2003
- 14 Balarajan Y, Selvaraj S, Subramanian SV. Health care and equity in India. Lancet 2011; 377: 505-15
- 15 Kurkure PA, Achrekar S, Uparkar U, Dalvi N, Goswami S. Surviving childhood cancer: What next? Issues under consideration at the after completion of therapy (ACT) clinic in India. Med Pediatr Oncol 2003; 41: 588-9
- 16 Mohanti BK, Kaur J. Living experiences of Indian adult cancer survivors – A brief report. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2015; 16: 507-12
- 17 Seth R. The after treatment completion card (ATCC): Medical passport for pediatric cancer survivors. Pediatr Hematol Oncol J 2018; 3: 88-9
- 18 Arora RS, Bakhshi S. Indian Pediatric Oncology Group (InPOG) – Collaborative research in India comes of age. Pediatr Hematol Oncol J 2016; 1: 13-7


 PDF
PDF  Views
Views  Share
Share

