Oral Mucositis with Abiraterone Acetate: A Therapeutic Dilemma
CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 · Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 2020; 41(05): 756-757
DOI: DOI: 10.4103/ijmpo.ijmpo_95_19
Abstract
Mucositis is a common complication of cancer treatment. Mucositis has varied etiology. Here, we describe a case of 71-year-old male with metastatic castrate-resistant carcinoma prostate who developed mucositis with the use of targeted therapy, and this particular scenario led to the therapeutic dilemma.
Publication History
Received: 10 April 2019
Accepted: 20 October 2019
Article published online:
17 May 2021
© 2020. Indian Society of Medical and Paediatric Oncology. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.)
Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
A-12, 2nd Floor, Sector 2, Noida-201301 UP, India
Abstract
Mucositis is a common complication of cancer treatment. Mucositis has varied etiology. Here, we describe a case of 71-year-old male with metastatic castrate-resistant carcinoma prostate who developed mucositis with the use of targeted therapy, and this particular scenario led to the therapeutic dilemma.
Keywords
Abiraterone acetate - metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer - mucositisIntroduction
Oral mucositis is one of the main complications of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Newer drugs including targeted therapy have a different spectrum of toxicity as compared to conventional cytotoxic agents. However, it is also not free from on-target and off-target toxicity including mucositis. Among the newer anticancer therapies, abiraterone acetate is a drug widely used in both castrate sensitive[1] and castrate-resistant prostate cancer.[2] Abiraterone is a CYP17 inhibitor and acts as an androgen synthesis inhibitor.[3] The common toxicities associated with abiraterone are hypokalemia, hepatitis, and hypertension.[1] Discontinuation of abiraterone in view of severe dermatological toxicity is known. However, discontinuation because of oral mucositis from abiraterone is not documented in the literature.[4] Here, we present a case of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) on abiraterone who developed oral mucositis with plaque-like lesions. To the best of our knowledge, we have not been able to come across a similar presentation of abiraterone toxicity in the literature.
Case Report
A 71-year-old male, chronic tobacco chewer and smoker, a known case of coronary artery disease, post coronary artery bypass grafting diagnosed as a case of mCRPC (Gleason 8), post bilateral orchidectomy (androgen deprivation therapy). He was on atorvastatin, metoprolol, diltiazem, clopivas, ecosprin, and ranolazine in view of his cardiovascular disease. He presented with a new onset of backache along with a rise in prostate-specific antigen levels, and on evaluation, he was found to have progressive disease. He received radiation therapy to the back and was started on abiraterone acetate along with prednisolone for mCRPC as he was reluctant to using docetaxel as a therapeutic option for his disease management. Within 2 weeks of prescribed medication, he presented to the hospital with complaints of burning painful sensation and lesions over the tongue which began 7–8 days after starting the medication. A personal or family history of atopy or allergic manifestation was ruled out. There was no history of intake of any new medication except abiraterone. On examination, he was oriented and alert, hemodynamically stable, and had poor oro-dental hygiene along with erythema of the tongue extending up to the soft palate [Figure 1]. He had plaque-like lesions over the ventral surface of the tongue [Figure 1]. His oral intake was restricted due to pain, and the patient was on a liquid diet. Severity of mucositis was Grade 3 as per CTCAE version 5.0 (Abirapro, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals, India). He was advised biopsy of the tongue lesion which he refused. Abiraterone acetate was stopped, doses of steroids were escalated, and antihistaminics were added. Oral topical steroid mouthwash was also started as per the dermatological consultation. His oral lesions gradually improved, and he was started on a routine diet. He was discharged with the resolution of his oral lesions.
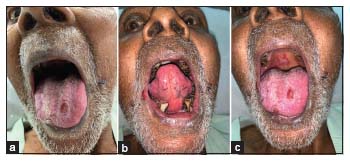
| Figure 1: (a) Erythematous lesions over the ventral surface of the tongue, (b) plaque-like lesion over the dorsal surface of the tongue, (c) plaque-like lesions over the palate
Discussion
Mucositis is a well-known toxicity of radiation therapy, cytotoxic agents, and targeted therapy. DNA damage and mitochondria-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species are induced by chemotherapy or radiotherapy which play a major role in the pathogenesis of mucositis.[5] The pathobiology of the oral mucositis is likely to be different from conventional cytotoxic agents and radiation, as it also differs in its manifestation and is commonly called as stomatitis. Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors, mTOR inhibitors, and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors all cause stomatitis in various proportions.[5] Other factors which also contribute to mucositis are hot food and drinks, sharp edges of teeth and ill-fitting prosthesis, poor oral hygiene, dose and regimen of chemotherapy used, and concurrent use of radiation and chemotherapy.
In our patient, poor oro-dental hygiene can be considered as a contributing factor. In view of the temporal association with the drug intake and positive dechallenge, the causality was assessed as probably based on the WHO–UMC scale. Rechallenge was not attempted because the patient refused for it. We have also tried to rule out a potential drug interaction. Rechallenge and tongue biopsy would have given us a definitive diagnosis.
Abiraterone acetate is a selective inhibitor of CYP 17; thereby, it inhibits androgen synthesis and signaling which is crucial in the pathogenesis of metastatic prostate cancer.[3] Abiraterone acetate has given survival advantage in the management of both castrate sensitive as well as castrate-resistant prostate cancer. It is one of the few options available for the management m CRPC. It is an oral drug which is given on an empty stomach in a dose of 1000 mg, however, as per recent evidence, it can be taken as 250 mg tablet with food.[6] We offered him a lower dose of abiraterone acetate (250 mg) along with low-fat food; however, he refused to take the same medicine again. He had already denied taking docetaxel and could not afford enzalutamide. This episode of severe oral mucositis with abiraterone acetate led to its discontinuation and led to a therapeutic challenge in the management of this patient.
Conflict of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fizazi K, Tran N, Fein L, Matsubara N, Rodriguez-Antolin A, Alekseev BY. et al. Abiraterone plus prednisone in metastatic, castration-sensitive prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2017; 377: 352-60
- Ryan CJ, Smith MR, Fizazi K, Saad F, Mulders PF, Sternberg CN. et al. Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone versus placebo plus prednisone in chemotherapy-naive men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (COU-AA-302): Final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16: 152-60
- Scott LJ. Abiraterone acetate: A review in metastatic castration-resistant prostrate cancer. Drugs 2017; 77: 1565-76
- Ramudo-Cela L, Balea-Filgueiras J, Vizoso-Hermida JR, Martín-Herranz I. Study of cases of abiraterone discontinuation due to toxicity in pre-chemotherapy after 1 year's experience. J Oncol Pharm Pract 2017; 23: 615-9
- Al-Ansari S, Zecha JA, Barasch A, de Lange J, Rozema FR, Raber-Durlacher JE. Oral mucositis induced by anticancer therapies. Curr Oral Health Rep 2015; 2: 202-11
- Szmulewitz RZ, Peer CJ, Ibraheem A, Martinez E, Kozloff MF, Carthon B. et al. Prospective international randomized phase II study of low-dose abiraterone with food versus standard dose abiraterone in castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 2018; 36: 1389-95
Address for correspondence
Publication History
Received: 10 April 2019
Accepted: 20 October 2019
Article published online:
17 May 2021
© 2020. Indian Society of Medical and Paediatric Oncology. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.)
Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
A-12, 2nd Floor, Sector 2, Noida-201301 UP, India

| Figure 1: (a) Erythematous lesions over the ventral surface of the tongue, (b) plaque-like lesion over the dorsal surface of the tongue, (c) plaque-like lesions over the palate
References
- Fizazi K, Tran N, Fein L, Matsubara N, Rodriguez-Antolin A, Alekseev BY. et al. Abiraterone plus prednisone in metastatic, castration-sensitive prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2017; 377: 352-60
- Ryan CJ, Smith MR, Fizazi K, Saad F, Mulders PF, Sternberg CN. et al. Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone versus placebo plus prednisone in chemotherapy-naive men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (COU-AA-302): Final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16: 152-60
- Scott LJ. Abiraterone acetate: A review in metastatic castration-resistant prostrate cancer. Drugs 2017; 77: 1565-76
- Ramudo-Cela L, Balea-Filgueiras J, Vizoso-Hermida JR, Martín-Herranz I. Study of cases of abiraterone discontinuation due to toxicity in pre-chemotherapy after 1 year's experience. J Oncol Pharm Pract 2017; 23: 615-9
- Al-Ansari S, Zecha JA, Barasch A, de Lange J, Rozema FR, Raber-Durlacher JE. Oral mucositis induced by anticancer therapies. Curr Oral Health Rep 2015; 2: 202-11
- Szmulewitz RZ, Peer CJ, Ibraheem A, Martinez E, Kozloff MF, Carthon B. et al. Prospective international randomized phase II study of low-dose abiraterone with food versus standard dose abiraterone in castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 2018; 36: 1389-95


 PDF
PDF  Views
Views  Share
Share

